Tracheostoma revision with flap rotation is a surgical procedure designed to address various medical conditions affecting the tracheostoma. This procedure involves rotating a local flap of tissue to reconstruct or reposition the tracheostoma, offering functional and cosmetic benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the indications, preoperative considerations, surgical technique, postoperative care, complications, outcomes, and case studies related to tracheostoma revision with flap rotation.
Indications for Tracheostoma Revision with Flap Rotation
Tracheostoma revision with flap rotation is indicated in several medical conditions or situations, including:
- Tracheal stenosis, a narrowing of the tracheal lumen
- Tracheomalacia, a weakening of the tracheal wall
- Tracheal fistula, an abnormal connection between the trachea and another structure
- Tracheal diverticulum, a sac-like protrusion from the tracheal wall
- Tracheal atresia, a congenital malformation where the trachea is incompletely formed
Preoperative Considerations
Prior to tracheostoma revision with flap rotation, a thorough preoperative assessment and preparation is essential.
This includes:
- Patient evaluation:A detailed medical history, physical examination, and assessment of the tracheostoma and surrounding tissues.
- Imaging studies:Imaging studies such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be performed to evaluate the tracheal anatomy and any associated abnormalities.
- Other necessary measures:Other measures such as pulmonary function testing, bronchoscopy, or laryngoscopy may be performed to assess the patient’s respiratory function and vocal cord mobility.
Surgical Technique
The surgical technique for tracheostoma revision with flap rotation typically involves the following steps:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Anesthesia: General anesthesia is typically used. |
| 2 | Incision: A horizontal or vertical incision is made over the tracheostoma. |
| 3 | Flap design: A rectangular or triangular flap is designed based on the size and location of the tracheal defect. |
| 4 | Flap mobilization: The flap is carefully dissected and mobilized from the surrounding tissues. |
| 5 | Closure: The flap is rotated and sutured into place to cover the tracheal defect. |
Postoperative Care
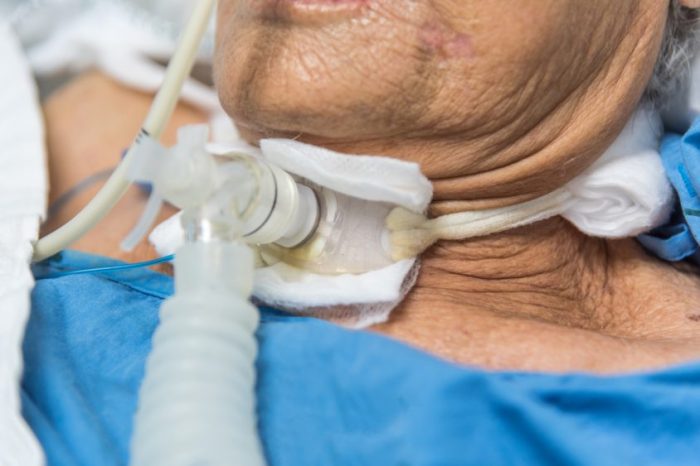
Postoperative care following tracheostoma revision with flap rotation involves:
- Wound care:The surgical wound is monitored for infection and healing.
- Monitoring:The patient’s respiratory status and vital signs are closely monitored.
- Follow-up appointments:Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to assess the healing process and monitor for any complications.
Complications
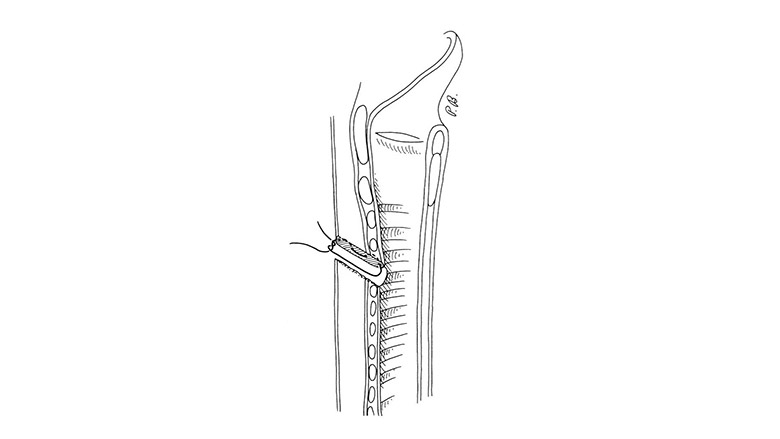
Potential complications associated with tracheostoma revision with flap rotation include:
- Hemorrhage
- Infection
- Tracheal stenosis
- Tracheomalacia
- Flap necrosis
Outcomes
The success rates and outcomes of tracheostoma revision with flap rotation vary depending on the underlying condition and the individual patient.
In general, the procedure is associated with improved airway patency, reduced respiratory symptoms, and improved quality of life.
Case Studies
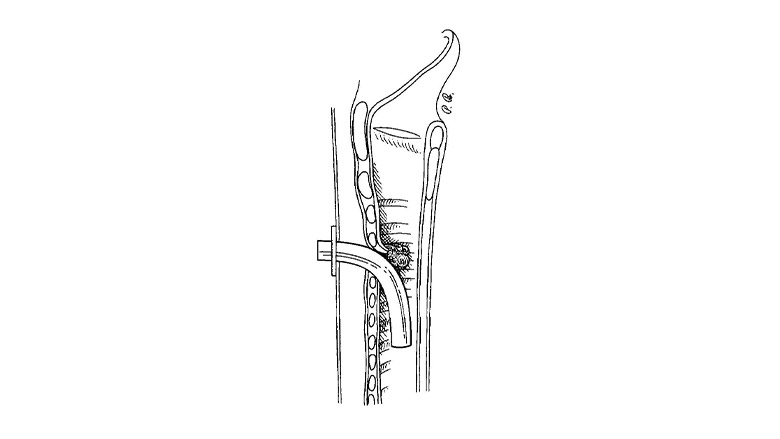
Case Study 1:A 65-year-old male with a tracheal stenosis underwent tracheostoma revision with flap rotation. The procedure resulted in a significant improvement in his respiratory function and a reduction in his tracheal stenosis.
Case Study 2:A 40-year-old female with a tracheomalacia underwent tracheostoma revision with flap rotation. The procedure resulted in a stabilization of her tracheal wall and a reduction in her respiratory symptoms.
FAQ Compilation: Tracheostoma Revision With Flap Rotation
What are the common indications for tracheostoma revision with flap rotation?
Tracheostoma revision with flap rotation is indicated in cases of tracheostoma stenosis, tracheomalacia, tracheocutaneous fistula, and other conditions that affect the function or aesthetics of the tracheostoma.
What are the key steps involved in the surgical technique for tracheostoma revision with flap rotation?
The surgical technique involves creating a local flap, mobilizing it, and rotating it to cover or reposition the tracheostoma. The flap is then sutured into place to secure the new tracheostoma opening.
What are the potential complications associated with tracheostoma revision with flap rotation?
Potential complications include bleeding, infection, flap necrosis, and tracheal stenosis. However, these complications are relatively rare when the procedure is performed by experienced surgeons.